There are Different Types of Lupus: They are,
- Systemic lupus erythematosus: The most common can be mild or severe and can harm many parts of the body.
- Discoid lupus: This type of lupus causes a rash on the skin that does not go away.
- Subacute cutaneous lupus: Causes blisters after sun exposure.
- Drug-Induced Lupus: It may cause by some medicines. In standard cases, when the drug in question stops, the disease disappears.
- Neonatal lupus: It is not a common disease and affects newborns. Specific antibodies may cause it in the mother.
Table of Contents
Prognosis of The Disease
Currently, medical science has not yet achieved any method to cure lupus; this disease even today registers deaths in patients who have not received adequate treatment. Despite everything, if the treatment is successful, it is rare for a patient to die from lupus; even 80-90% of patients diagnosed with lupus live more than ten years after knowing that they have the disease. On the other hand, patients who have some organs affected by the disease but whose life is not at risk usually enjoy a completely everyday life if they follow the advice of their Specialist:
- Take prescribed medications.
- Seek help in case the effects are undesirable or new symptoms of the disease appear.
Symptoms of Lupus
Lupus can present different symptoms that depend on each person. The most common symptoms are usually:
- Joint pain or swelling
- Muscle pain.
- Fever without knowledge of the cause.
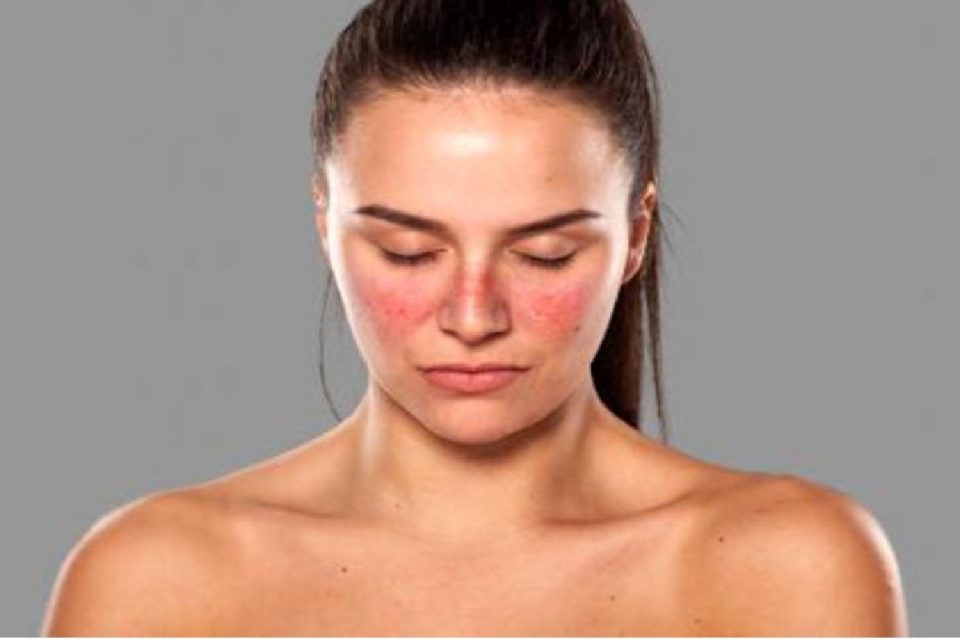
- Red rashes on the skin, mainly on the face and in the shape of a butterfly.
- Chest pain when you breathe deeply.
- Hair loss.
- White or purple fingers or toes.
- Sensibility in sunlight.
- Swelling in the legs or the eye area.
- Ulcers in the mouth
- Inflamed glands.
- Feeling extremely tired
These symptoms can come and go, and they are called “flare-ups.” These outbreaks can be mild or severe, and new symptoms can appear at any moment.
Medical Tests for Lupus
There is no single test to diagnose lupus, as with symptoms, because sometimes it can be confused with other diseases. It might take months or maybe years for a specialist to diagnose lupus. Some of the medical tests that the Specialist can use to diagnose lupus are:
- Medical history.
- Full examination.
- Blood test.
- Skin biopsy.
- Kidney biopsy .
What are the Causes of Lupus?
The cause and its risk factors arecurrently unknown. All people can have lupus. However, it tends to affect women more; it usually begins in youth and frequently in blacks, Asians, and Hispanic Americans. In addition, African American and Hispanic women are more susceptible to the more severe types.
Can Lupus Be Prevented?
It can appear without any symptoms, so it is difficult to know if it can ultimately prevent it in any way during a person’s life. The powerful thing a person can do is reduce the chances of lupus appearing by being mindful of eating a balanced diet and exercising, leading a healthy lifestyle.
- Take care of your diet: By only consuming the right foods, leading a healthy diet, you can prevent inflammation of the organs, precisely one of the main symptoms of lupus. It is also essential to ensure that the food you eat does not contain harmful chemicals, such as pesticides or medications.
- Exercise: Carrying out an active life and avoiding a sedentary lifestyle can help build endurance, control weight, and even improve mood. Review with your Specialist the type of exercise you can perform because the organs affected with lupus could complicate the practice of a specific activity.
- Take supplements: In this way, you can add nutritional value to your diet and help reduce inflammation throughout the body. Krill oil, for example, has nutrients that can cause improvements in your cardiovascular health through regular consumption.
Treatments For Lupus
There is no cure for lupus, but medications and lifestyle changes can help you take control of the disease.
Regarding the objectives of each treatment, they are:
- Avoid breakouts.
- Treat symptoms as soon as they appear.
- Reduce organ damage and other problems.
Medications to: may accompany the treatments
- Reduce inflammation and pain.
- Avoid or reduce breakouts.
- Help the immune system.
- Reduce or prevent damage to the joints.
- Balance hormones
In addition to having medicine for lupus, you may need to take medication for other problems related to the same disease, such as high cholesterol levels, high blood pressure, or some infections. On the other hand, there are alternative treatments that take a different path from conventional therapies. But at present, there is no medical research that reports on existing and valuable alternative therapies to combat lupus. Some alternative approaches or those that have a complementary function can help improve the quality of life of a chronic disease such as this one. Should remember that before carrying out any alternative treatment, you should consult with the Specialist in question.
What Specialist Treats It?
Patients will go through a variety of doctors. In the beginning, a primary care doctor will diagnose the disease and later go to a rheumatologist (Specialist in conditions that affect muscles and joints). Then the patient must be monitored by a rheumatologist or an internist with experience in the management of autoimmune diseases, who will guide the treatment, evaluating the efficacy, monitoring the appearance of side effects and complications. Occasionally, the participation of other specialties, such as dermatology, nephrology, or cardiology, may be required, depending on the affected organs. Given that it is a chronic disease, a good doctor-patient relationship is essential, providing the necessary information understandably so that the patient can participate in decisions about their treatment.

